VERBS PART 1
- Verbs are a class of words used to show the performance of an action (do, throw, run), existence (be),
possession (have), or state (know, love) of a subject. To put it simply a verb shows what something or
someone does.
- e.g : The dog bit the man.
( bit is the verb and the word which shows the action of the sentence.)
- The verb is perhaps the most important part of the sentence.
- The verb or compound verb is the critical element of the predicate of a sentence.
- Examples of verbs and compound verbs.
> Dracula bites his victims on the neck. (The verb "bites" describes the action Dracula
takes.)
> They will meet us at the newest cafe. (the compound verb "will meet" describes an action
that will take place in the future.)
> My first teacher was Miss Crowford. (verb "was" the simple past tense of "is") identifies a
particular person).
> Karl Creelman bicycled around the world in 1899, but his diaries and his bicycle were
destroyed. (describes an action which took place in the past.)
examples;
3 MAJOR CLASSES OF VERBS
1) LEXICAL VERBS/ FULL VERBS
- Is the main verb of the sentence.
- Have regular endings for forming present and past tense (call, calls, called)
- Most common lexical verbs in English have irregular morphology.
- The verbs be, have, and do...all three of which can function as main verbs or auxiliary
verbs.
- Main verb function :
e.g : He does his homework daily.
His dad was an art professor.
- Auxiliary verbs .
- Auxiliary verb function (with main verb underlined) :
e.g : I didn't invent Irish dancing.
We are all worms, but I do believe I am a glowworm.
I was wearing a dark ski mask.
- Modal auxiliary (helping auxiliary)
- Expresses necessity, uncertainty,ability, or permission.
- e.g : Will and would
Shall and would
May and might
Can and could
Must and have to
Ought to and had better
1) VERBS ABOUT MENTAL ACTIVITIES
- believe, forget, know, notice,remember, understand.
- e.g : I believe in God
I don't recognise him.
2) VERBS DESCRIBE EMOTIONAL STATE
- desire, love, like, hate, prefer, want
- e.g : She loves him.
He wants a new toy.
3) CERTAIN OTHER VERBS
- belong, cost, fit, include, mean, need, own, matter
- e.g : This book belongs to e.
The ticket cost five pounds
4) VERBS OF PERCEPTION
- see, hear, taste, smell, feel (5 senses)
- e.g : I can't hear you.
Can you smell the scent of the roses?
> SOME OTHER ENGLISH STATIVE VERBS
- Denote states rather than actions
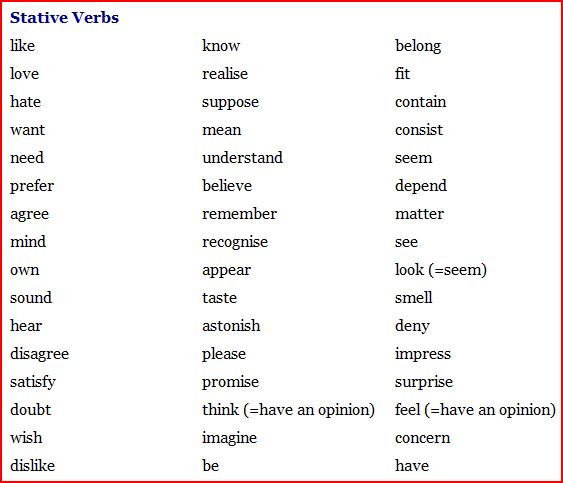
- Verbs 'have' and 'be' are usually stative can be dynamic in certain situations.
- Think is stative when it means 'believe', but not when it means 'consider'.
- e.g of non-stative verbs : You are being silly.
She is having a baby.
I am thinking.
1) PRESENT SIMPLE

- Present simple are use for thoughts and feeling, state of being, facts and things that
are true for a long time.

> - A present state which exist now and a fact that always true.
- Something was true in the past, is true now and will be true in the future.
- e.g : The world is round.
> - A present habit/ an action we repeat regularly.
- e.g : My class start at nine.
> - A present event(which happens at the moment of speaking.
- e.g: I regret that I made a mistake.
2) PRESENT CONTINUOUS
 \
\
- For something happening now.
- e.g : I am speaking to you.
- For a routine or a situation that we see as temporary.
- e.g: I'm working at a sport shop for six weeks.
- Always
- e.g : Tom is always inviting friends home.
- Positives, negatives, and questions forms
| affirmative | negative | question | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | I am playing. | I am not playing. | Am I playing? |
| he, she, it | He is playing. | He is not playing. | Is he playing? |
| you, we, they | You are playing. | You are not playing. | Are you playing? |
- Forms of the present tense
3rd person singular all others
He works I work
She works You work
The boss works we work
The telephone(it works ) they work
Her friend works Her friends work
- I am/ have/ do/ say (e.g: I don't like sweet.)
- We/ you/ they/ are/ have/ do/ says (e.g: We have pets.)
- He/ she/ it/ has/ does/ says (e.g: Siti has a pet.)




No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.